Visual designers are the creative professionals who create the aesthetics and user experience of digital media. They transform ideas into eye-catching designs that captivate and enhance the user experience by using intricate tools and techniques. As businesses strive to capture attention in a competitive marketplace, a visual designer's expertise is essential in crafting compelling and impactful visual narratives.
At Aloa, we deliver top-notch software projects through our expertly crafted project management framework. We partner with the best development teams and use cutting-edge technology and trends to bring your vision to life. Our transparent performance reports and a dedicated U.S.-based product owner ensure you stay informed and supported through the entire software journey, from initial consultations to project launch.
Leveraging our experience hiring top-tier software development and design teams, this guide delves into the specialized skills and tools distinguishing visual designers from other creative professionals. After reading, you’ll understand what sets them apart from graphic designers and their unique approach to creating engaging digital interfaces so you can determine if you need one in your team.
Let’s get started!
What is a Visual Designer?
A visual designer is a professional who creates and maintains a brand's visual identity across websites and mobile apps. They use their expertise in color theory, typography, and design tools to produce compelling visuals that enhance brand recognition and user engagement.
Key Responsibilities of a Visual Designer
Visual designers have a diverse set of responsibilities tailored to the client’s unique goals:

- Develop and maintain a consistent visual identity for a brand across digital and print media.
- Create and iterate on user interface (UI) design that focuses on user experience and accessibility.
- Manage multiple design projects simultaneously while ensuring timely delivery and high standards.
- Collaborate with cross-functional teams, including web developers, UX designers, and marketers, to ensure consistency in design.
- Research about design to stay updated with the latest design trends and technologies.
- Produce high-quality visual content using industry-standard tools like infographics, images, and icons.
- Present prototypes and design concepts to stakeholders and gather feedback for revisions.
- Ensure visual designs adhere to the brand's guidelines and project specifications.
- Create mockups and wireframes to illustrate design concepts and user flows.
- Collaborate with developers to finalize the product's accurate implementation of visual designs.
Visual vs. Graphic Designers
Both visual and graphic designers create digital media content, but their roles, tools, and processes differ significantly. Here's a clear overview:
Distinct Roles in Evolving Media
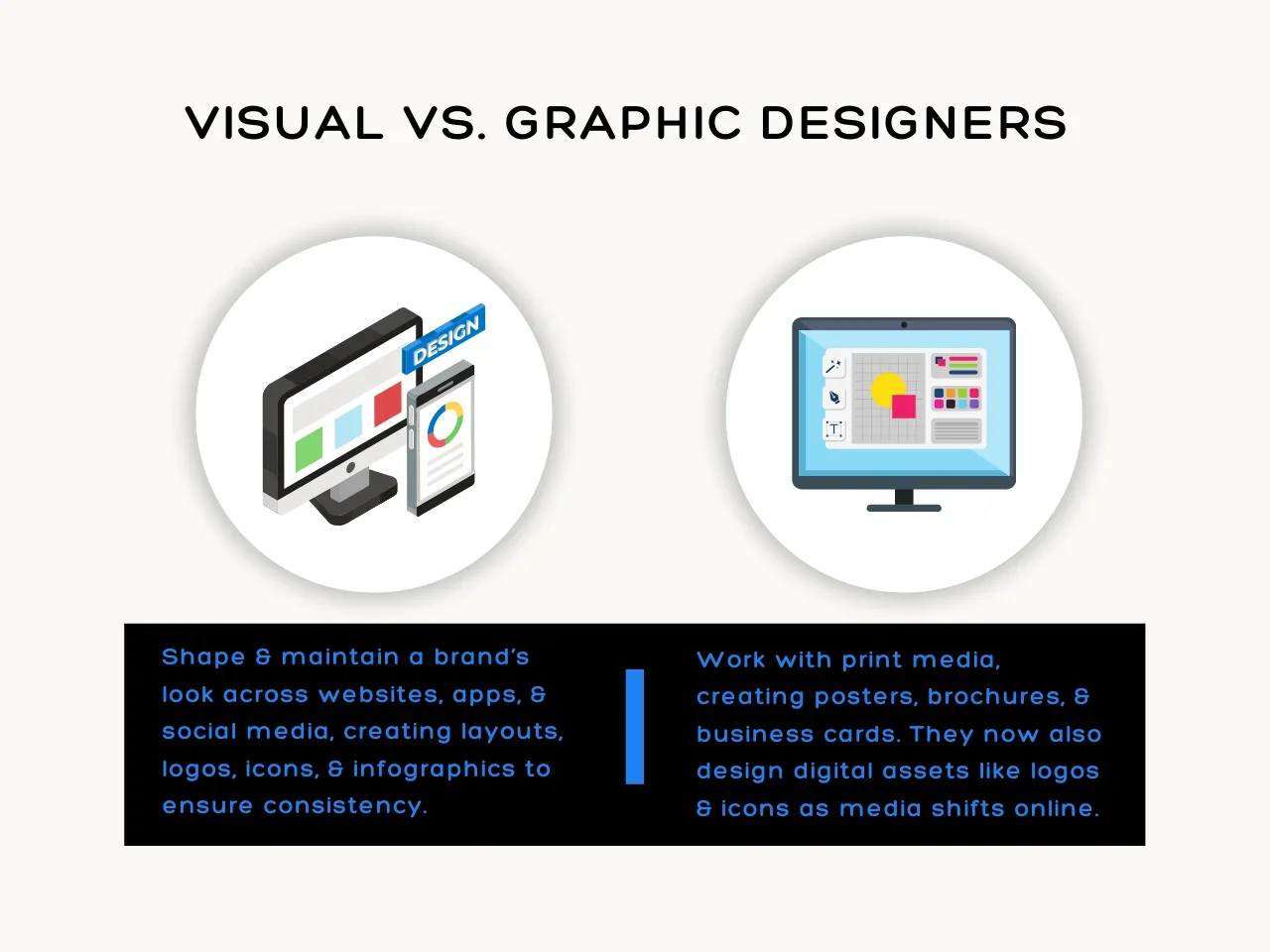
Visual designers focus on shaping and maintaining a brand’s appearance on websites, applications, and social media. They create layouts, logos, icons, infographics, and presentation materials to keep the brand consistent.
In contrast, graphic designers work with print media. They produce posters, brochures, and business cards by creating a digital copy of the content which are then sent to a print shop—or processed through a Shopify web to print system—to produce the physical copies. However, as media has shifted online, their work now includes digital assets like logos and icons, with many designers turning to a logo maker to simplify the process.
Exploring Tools and Processes
Visual designers use a wider range of tools than graphic designers because their role involves more aspects of design and development. While graphic designers primarily use Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign to create static visuals, visual designers use additional tools. In some cases, they prefer Photoshop alternatives that offer simpler interfaces or more affordable pricing for everyday design tasks. These include prototyping tools like Adobe XD or Figma for interactive designs and motion graphics software like After Effects for animations.
When it comes to processes, web designers focus on collaborating with marketing, product management, and other designers. As remote work grows, virtual feedback is also important. Despite the fast-paced industry changes, designers enjoy seeing their ideas succeed.
Graphic designers, on the other hand, outline a goal and conduct thorough research to understand the market and user needs. They then brainstorm and refine ideas through reviews and iterations. The process ends with stakeholder approval and user testing to ensure the final design meets the business requirements.
Similarities and Differences of Visual and Graphic Designers
If you're still trying to understand the differences between visual and graphic designers, graphic designers focus primarily on creating specific visual elements and materials. They develop logos, marketing collateral, and web designs from start to finish, applying their skills in Photoshop and Illustrator. However, with tools like an AI logo generator, businesses can now quickly create professional looking logos even without advanced design expertise.
Visual designers are more concerned with the user experience and overall visual communication. They may help select fonts and color schemes but are less involved in creating these elements. They ensure that all visual aspects align with the brand’s identity and specific user interface needs.
Despite the different focuses of these job titles, both visual and graphic designers share specific skills:

- Problem-Solving: Innovative in meeting project requirements and solving new design challenges.
- Passion for Design: Fuel creativity and drive compelling work through a deep appreciation for art and design.
- Visual-Spatial Intelligence: Perceives and understands visual elements to create aesthetically pleasing and functional designs.
- Time Management: Organizes and plans effectively to meet deadlines and handle multiple tasks efficiently.
- Technical Proficiency: Expertise in web design principles and coding languages, including responsive design, user interface considerations, HTML, and CSS.
- Visual Design Jobs: Works on print and digital platforms like book covers, billboards, digital advertisements, websites, and mobile apps.
A Day in the Life of a Visual Designer
If you are curious about what a visual designer’s day looks like, here’s a glimpse into their usual daily routine:
Creative Process: Conceptualization to Execution
Visual designers are skilled at understanding project briefs, developing design ideas, and creating precise visuals. They often present their designs to other departments, explaining the key features and benefits.
A visual designer’s daily tasks can vary depending on their experience level:
- Entry-Level Designers: Focus on following design ideas and learning basic design principles.
- Mid-Level Designers: Handle more complex projects and may start leading design efforts.
- Senior Designers: Develop creative strategies, mentor junior designers, and shape the brand’s direction.
Visual designers should also participate in brainstorming ideas and design reviews. They must communicate well with other teams to ensure designs meet technical requirements.
Collaboration and Feedback
A visual designer creates the visuals and layout for digital projects based on the client’s needs and meeting discussions. They collaborate with teams from marketing, development, IT, and operations.
Working together on the design keeps the client involved and lets them suggest changes early on. It also helps prevent problems later, like if the design is hard to build, doesn’t meet legal requirements, or is missing important marketing details.
Clear communication between designers and other team members ensures the project's smooth flow. The best way is to use a communication tool like Trello, Miro, or Slack to avoid confusion and delays.
Problem Solving and Revisions
Visual designers excel in creating visually compelling representations of ideas using various design elements like type, space, and color. Effective visual design involves more than just form; it requires adhering to industry best practices and analyzing problems to craft meaningful solutions. Designers must also be open to feedback and adapt their work based on client or team input.
Designers often deal with numerous client revisions, which can extend project timelines and disrupt personal schedules. This constant cycle of changes can lead to unpredictable work hours, making it challenging to balance personal life. Setting realistic deadlines and communicating openly with clients about the time needed for quality work is essential for managing these demands.
Balancing Creativity and Deadlines
The visual designer role requires creativity in using color, lines, typography, and white space to create unique and impactful designs. To stand out in a competitive market, these digital designers must think outside the box, which requires imagination and a willingness to take risks. They must also be adaptable, as projects often change and new challenges arise.
For those on a career path in visual design, the visual designer job description usually includes the ability to multitask and meet deadlines, especially when working under pressure and as part of a team. Success in this field means managing deliverables effectively and embracing design work's fast-paced, ever-evolving nature.
Tools of the Trade for Visual Design
Visual designers use many tools to bring their creative ideas to life by creating branding, digital products, or marketing materials. These tools span multiple categories, including those utilized by animators. Here are some of the tools visual designers mostly use.
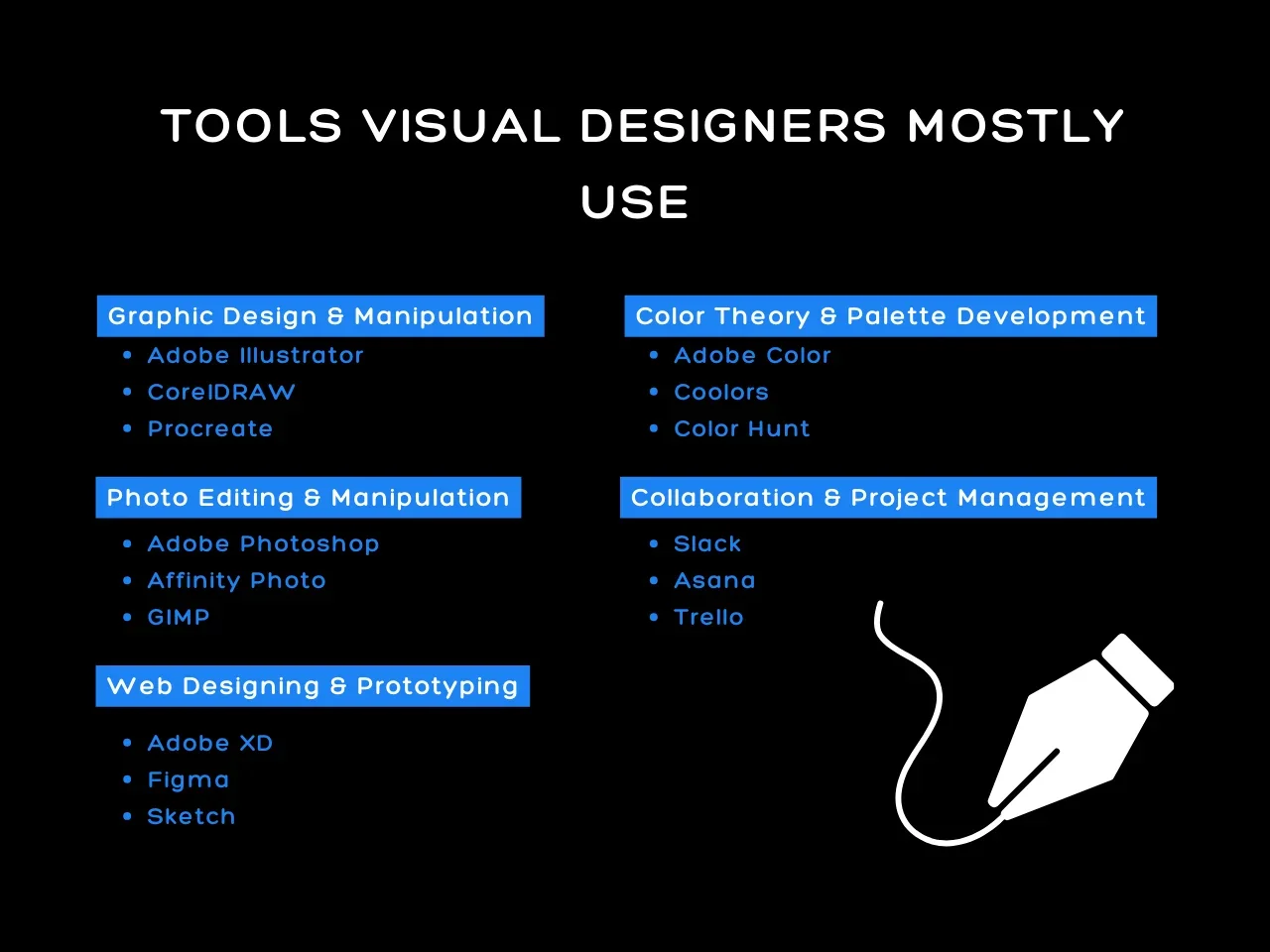
Graphic Design and Manipulation
Visual designs rely on various tools to create and manipulate visuals. These include:
- Adobe Illustrator: Creates and manipulates vector-based designs and illustrations. It’s widely used for creating logos, icons, and detailed artwork.
- CoreIDRAW: Provides powerful vector illustration tools for a wide range of projects
- Procreate: Offers natural drawing experience with an extensive brush library.
Photo Editing and Manipulation
Visual designers use photo editing and manipulation tools to access advanced features for retouching, compositing, and ensuring high-quality visual content.
- Adobe Photoshop: Offers extensive tools for image manipulation, compositing, and retouching to create polished visual content
- Affinity Photo: Provides robust photo editing features and non-destructive workflows. It’s a cost-effective alternative to Photoshop.
- GIMP: Provides a comprehensive set of tools for retouching and image composition.
- YouCam Online Editor: Offers AI web-based image editing tools that enables easy, professional-quality photo editing directly in your browser.
Web Design and Prototyping
Visual designers leverage web design and prototyping tools to streamline the design process from concept to final prototype.

- Adobe XD: Designs and prototypes user experiences for web and mobile devices and apps. It streamlines the design process from ideation to final prototype.
- Figma: Supports real-time co-editing and prototyping to enhance teamwork and efficiency in design projects. It’s user-friendly and has cloud-based collaboration features.
- Sketch: Focuses on user interface and experience design. It’s ideal for creating wireframes and mockups that are only available for Mac users.
Color Theory and Palette Designs
Visual designers need color theory and palette design tools to add depth to their projects, making sure that the color choices evoke the right emotions.
- Adobe Color: Allows web designers to develop and share color palettes easily, ensuring color harmony in design projects.
- Coolors: Helps designers create aesthetically pleasing color palettes.
- Color Hunt: Provides a curated collection of color palettes created by the design community.
Collaboration and Project Management
Visual designers use collaboration and project management tools to plan and organize workflows through boards and lists.
- Slack: Supports team communication through channels, direct messaging, and integrations with tools like Asana and Google Drive. With Slack promo codes, businesses can access premium features at a lower cost, enhancing collaboration and productivity across teams.
- Asana: Features timelines, task assignments, and progress tracking. This project planning and task management platform helps teams stay organized and meet deadlines.
- Trello: Uses boards, lists, and cars to organize and track projects and manage tasks and workflows.
Key Takeaway
Visual designers are invaluable assets to marketing and creative teams. They bring creativity and technical expertise that can benefit digital and print media. Their talents are pivotal in shaping your brand’s visual identity while ensuring consistency and engagement with target audiences.
However, visual web designers may have diverse skill sets, experience, and areas of expertise. Some may excel in user interface design, while others specialize in branding or motion graphics. Not every candidate will be the perfect fit for your team. So, select whose expertise aligns with your specific needs and the project's complexity.
If you’re looking to boost your brand’s identity and collaborate with top-notch design talent, Aloa is here to make it happen. We know hiring can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, so we leverage our network of highly vetted partners to connect you with the best talent. Our outsourcing strategies help you work with a visual designer who can expertly enhance your brand’s identity. Contact us via [email protected] to get started!

