The year 2024 has brought about significant changes in the field of education. With the rapid advancement of technology, educational institutions are leveraging the power of Edtech to transform traditional learning methods. Understanding educational technology and its implications is more critical than ever in this dynamic landscape.
Aloa specializes in guiding organizations in harnessing the power of technology to improve education. It's an evolving ecosystem that includes e-learning, learning management systems, gamification, and immersive experiences through virtual and augmented reality. Aloa helps organizations navigate this ever-changing terrain, ensuring they stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
In this blog, we will explore the multifaceted world of Edtech in 2024, encompassing various types. You will learn how educational technology shapes education's future and the key considerations to ensure its success. We'll also highlight the intersection of software development and educational technology.
Embracing these opportunities and challenges is essential to navigating educational technology's exciting yet complex journey in 2024. Let's dive in!
What is Edtech?
Edtech (Educational Technology) signifies the application of technology to advance teaching and learning, irrespective of traditional educational environments. This integration encompasses various digital tools, software, and online platforms. Educational technology harnesses the power of the internet, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning to revolutionize education.
Educational technology holds immense potential to revolutionize education. It can democratize access to learning, transcending geographical boundaries and socio-economic disparities. With AI and tech-driven instructional design, personalized learning experiences cater to individual learner needs, boosting educational outcomes.
Moreover, educational technology's influence extends to higher education, benefiting college students with online resources, collaborative platforms, and interactive learning materials. It fosters professional development through webinars, podcasts, and email communication. Even in the physical classroom, educational technology augments teaching methods, making lessons engaging and adaptive.
How to Leverage Edtech Solutions Into Your Business
Integrating Edtech solutions into your business can yield numerous benefits, from improving employee skills and productivity to enhancing customer interactions and experiences. Let's explore a step-by-step guide on effectively leveraging educational technology solutions into your business operations, regardless of your industry.
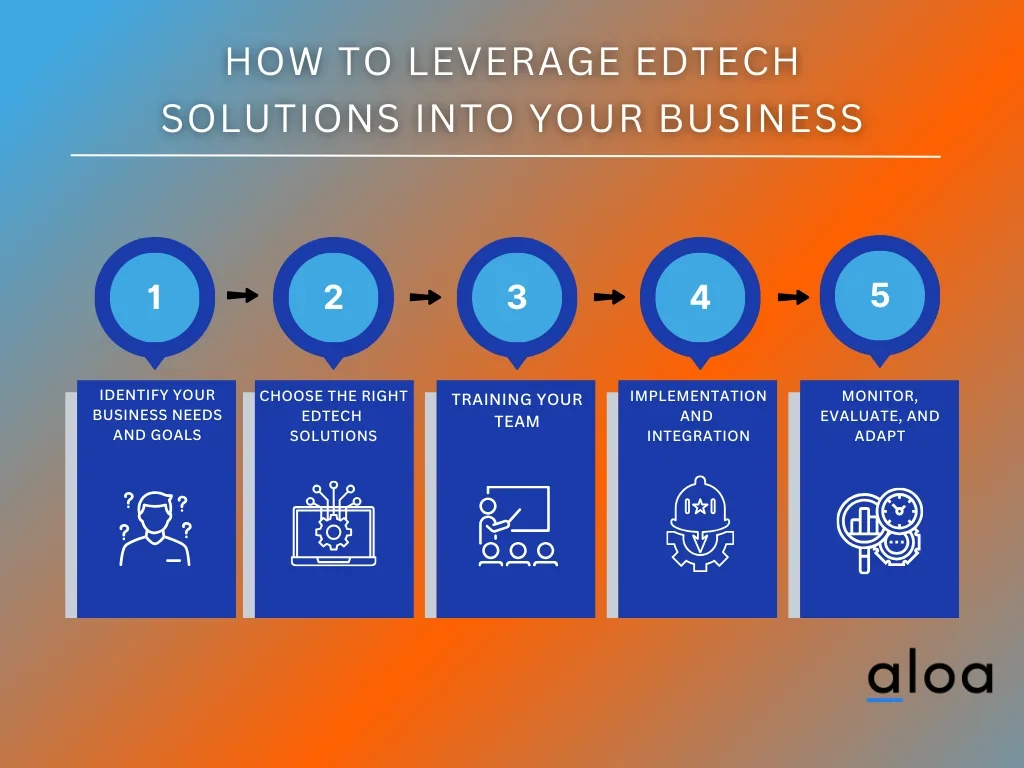
Step 1: Identify Your Business Needs and Goals
The first and most crucial step in integrating Edtech into your business is identifying your organization's needs and goals. What specific challenges do you aim to address, and what outcomes are you looking to achieve? Conduct a comprehensive assessment to determine areas where educational technology can positively impact.
Consider factors such as:
- Employee Training: Are there skill gaps within your workforce that educational technology can help bridge?
- Customer Engagement: How can educational technology enhance your customer interactions and experiences?
- Operational Efficiency: In what ways can educational technology streamline your business processes and improve overall efficiency?
Once you've identified your specific needs and goals, you can select the most relevant Edtech solutions that align with your business objectives.
Step 2: Choose the Right Edtech Solutions
With your business needs and goals in mind, the next step is to choose the appropriate educational technology solutions. This involves researching and evaluating various options available in the market.
Consider the following factors when selecting educational technology solutions:
- Relevance: Ensure the educational technology tools address your identified needs and goals.
- User-Friendly Interface: Opt for intuitive, user-friendly solutions that facilitate quicker organizational adoption.
- Scalability: Assess whether the educational technology solutions can grow alongside your business, accommodating increased demands and users.
- Cost-effectiveness: Evaluate the cost versus benefits to determine the ROI of the educational technology solutions.
Remember that Edtech is a vast field, and the right solution will depend on your industry, the size of your business, and the specific challenges you aim to overcome.
Step 3: Training Your Team
Implementing educational technology solutions in your business often requires employee training and onboarding. Ensure that your staff is well-prepared to use the technology effectively. This may involve:
- Training Programs: Develop or subscribe to training programs and consider using mentor mentee matching software to familiarize your employees with the educational technology tools. This can be done through online courses or on-site training sessions.
- User Support: Provide a support system for your employees to address their questions and concerns. This can include a dedicated support team or user guides and resources.
- Testing and Feedback: Encourage employees to test the educational technology solutions and provide feedback. This can help refine the implementation process and ensure the tools meet your business's needs.
Step 4: Implementation and Integration
Once your staff is prepared, it's time to implement and integrate the chosen Edtech solutions into your business operations. This process will vary based on the specific technology but may involve the following:
- Data Migration: If applicable, transfer relevant data from existing systems to the educational technology tools.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Ensure the new technology integrates seamlessly with your current business systems to avoid disruptions.
- Customization: Tailor the educational technology solutions to meet the unique requirements of your business.
It's essential to have a clear implementation plan that outlines roles and responsibilities, timelines, and key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the success of the integration.
Step 5: Monitor, Evaluate, and Adapt
The final step is an ongoing one. It involves continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation of the Edtech solutions within your business. This ensures they remain effective and aligned with your evolving needs and goals.
Consider the following practices:
- Data Analysis: Regularly analyze data generated by the educational technology tools to assess their impact on your business. This can include employee performance, customer engagement, or operational efficiency metrics.
- Feedback Loops: Establish feedback mechanisms where employees can report issues, suggest improvements, and share their experiences with the technology.
- Updates and Upgrades: Stay informed about updates and upgrades to the Edtech solutions. Ensure that your business is using the latest features and capabilities.
- Scalability: As your business grows, evaluate whether the educational technology solutions can scale accordingly. If necessary, consider additional training and support for new employees.
Incorporating educational technology solutions into your business is a dynamic process that requires ongoing attention and adaptation. By following these steps and embracing a culture of learning and improvement, your business can harness the full potential of educational technology to drive growth and success.
Types of Edtech
Edtech is rich and diverse, encompassing various types and sectors collectively shaping the educational landscape. This section will delve into specific types of educational technology, exploring their significance, use cases, and considerations for implementing these technologies in your educational or business settings.
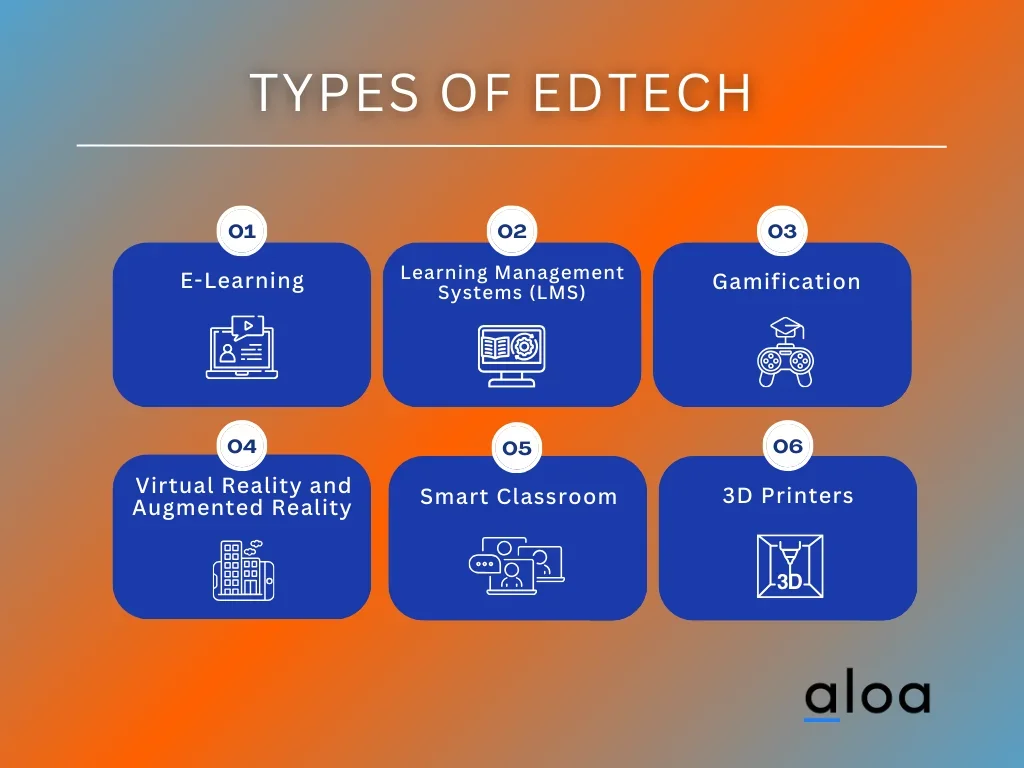
E-Learning
E-Learning stands at the forefront of the educational technology revolution. It involves using digital platforms and resources to facilitate remote learning, transcending geographical boundaries and traditional classroom constraints. The adoption of E-Learning has skyrocketed in recent years, and it plays a pivotal role in the education sector, catering to students of all ages, from K-12 to higher education.
Use Cases of E-Learning
- Online Courses: E-Learning platforms offer a vast array of online courses, covering subjects ranging from computer science to art history. These courses provide learners with flexibility and convenience, allowing them to acquire new skills or enhance existing ones at their own pace.
- Virtual Classrooms: Virtual classrooms replicate the traditional classroom experience in a digital setting. They enable real-time interaction between students and educators, facilitating discussions, collaborative projects, and immediate feedback.
- Digital Libraries: E-Learning platforms often include extensive digital libraries, where students can access many educational resources, including textbooks, research papers, and multimedia content. These libraries are instrumental in fostering self-directed learning.
When integrating E-Learning into your educational or business framework, it's crucial to address concerns related to data security and the digital divide. Ensuring that sensitive student or user data is protected is paramount. Additionally, efforts should be made to bridge the digital divide to ensure that everyone, regardless of their socioeconomic status or geographical location, has equal access to educational resources and opportunities.
Learning Management Systems (LMS)
LMS, or Learning Management Systems, offer a systematic approach to managing educational content, administrative tasks, and tracking student progress. These platforms are used extensively in educational institutions and corporate training, offering a streamlined way to deliver and track learning materials.
Use Cases of Learning Management Systems (LMS)
- Course Creation and Delivery: LMS platforms provide tools for educators and trainers to create, structure, and deliver courses. This ensures a consistent and organized learning experience for students or employees.
- Progress Tracking: LMS systems enable the tracking of students' or employees' progress, including assessment scores, participation, and completion of assignments. This data assists educators and trainers in understanding the strengths and weaknesses of their learners.
- Administrative Efficiency: LMS platforms simplify enrollment management, course scheduling, and resource allocation tasks. This efficiency is particularly valuable for institutions with many students or employees.
Compatibility with existing systems and the ease of use for educators/trainers and learners are critical considerations when adopting LMS. Scalability is also essential, especially for educational institutions and businesses expecting growth. Ensuring that the chosen LMS aligns with the organization's objectives and offers sufficient support for technical issues is equally important.
Gamification
Gamification introduces game elements into education, making learning more engaging and enjoyable. Educators aim to motivate students and enhance their learning experience by incorporating points, badges, and leaderboards.
Use Cases of Gamification
- Engagement: Gamification fosters engagement by making learning interactive and fun. This approach is efficient in K-12 education, where students are more likely to stay focused and enthusiastic about their studies.
- Motivation: Leaderboards and rewards systems motivate learners to achieve their goals. Students are encouraged to continue their educational journey when they see their progress and achievements.
- Skill Development: Gamified lessons often focus on skill development, allowing students to practice and improve in a safe and entertaining environment. This can be applied to various subjects, from language learning to math.
The challenge is finding the right balance between fun and educational value. Educators must ensure that the game mechanics align with their educational objectives. Designing inclusive games that cater to a diverse range of learners, including those with different learning styles and abilities, is also important. Additionally, it is essential to monitor and adjust the gamified elements to maintain their effectiveness over time.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies transport learners into immersive digital environments or enhance real-world experiences with digital information. These technologies have immense potential to revolutionize education, making it more interactive and experiential.
Use Cases of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
- Immersive Field Trips: VR can take students on virtual field trips to explore historical landmarks, dive into the ocean's depths, or travel to outer space. AR can overlay information on real-world objects, providing context and enhancing the learning experience.
- Science Simulations: VR and AR are used in science education to simulate complex experiments and phenomena. Students can interact with virtual molecules, dissect virtual organisms, and experiment in a controlled environment.
- Real-World Applications: AR is being employed in industries such as healthcare and engineering, offering hands-on training experiences. For example, medical students can use AR to practice surgical procedures in a simulated environment.
The hardware and content development costs can be a significant barrier. Educational institutions and businesses need to assess their budget and long-term sustainability. Additionally, addressing potential health issues, such as motion sickness in VR, is essential. Developing high-quality content and hardware compatibility should be carefully considered to ensure a seamless and practical learning experience.
Smart Classroom
Smart Classrooms leverage technology to create more interactive and engaging learning environments. They equip traditional classrooms with modern technology, such as interactive whiteboards, digital projectors, and specialized software, transforming how educators teach and students learn.
Use Cases of Smart Classrooms
- Interactive Learning: Smart classrooms enable interactive learning by allowing educators to use digital tools to present lessons. Students can engage with the content through touch-screen displays and interactive activities, promoting participation.
- Remote Learning Integration: Smart classrooms can connect with remote students, offering a blended learning approach. This is especially crucial during times of crisis, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, allowing students to access education from home.
- Data Analytics: They collect data on student engagement and participation, helping educators tailor their teaching methods to suit individual and group needs better.
Implementing smart classrooms requires both financial and technical considerations. Educational institutions must invest in the necessary hardware and software, and educators should receive training on effectively using these tools. Privacy and data security concerns are also significant, given that student data collection must be handled carefully.
3D Printers
3D Printing has made significant inroads into education, with 3D printers becoming valuable tools for teaching various subjects. They allow students to transform digital designs into tangible objects, providing hands-on experience and enhancing creativity.
Use Cases of 3D Printers
- Prototyping and Design: In engineering and product design courses, 3D printers enable students to create prototypes and visualize their designs in a tangible form.
- Science Experiments: In science classes, 3D printers can produce models of complex structures, making it easier for students to understand intricate scientific concepts.
- Art and Creativity: 3D printing encourages creativity in art classes. Students can design and print sculptures and other art pieces, fostering artistic expression.
The cost of 3D printers and the associated materials can be a barrier for some educational institutions. Maintenance and safety protocols are essential, as 3D printers involve heating elements and moving parts that could pose risks. Additionally, educators should be trained to use 3D printing technology and integrate it effectively into their curricula.
Practical Applications of Educational Technology
Educational Technology has revolutionized the way we approach learning and teaching. Its practical applications have transformed the education landscape, offering innovative solutions to enhance the learning experience. Let's explore six vital practical applications of Educational Technology that have significantly impacted education.
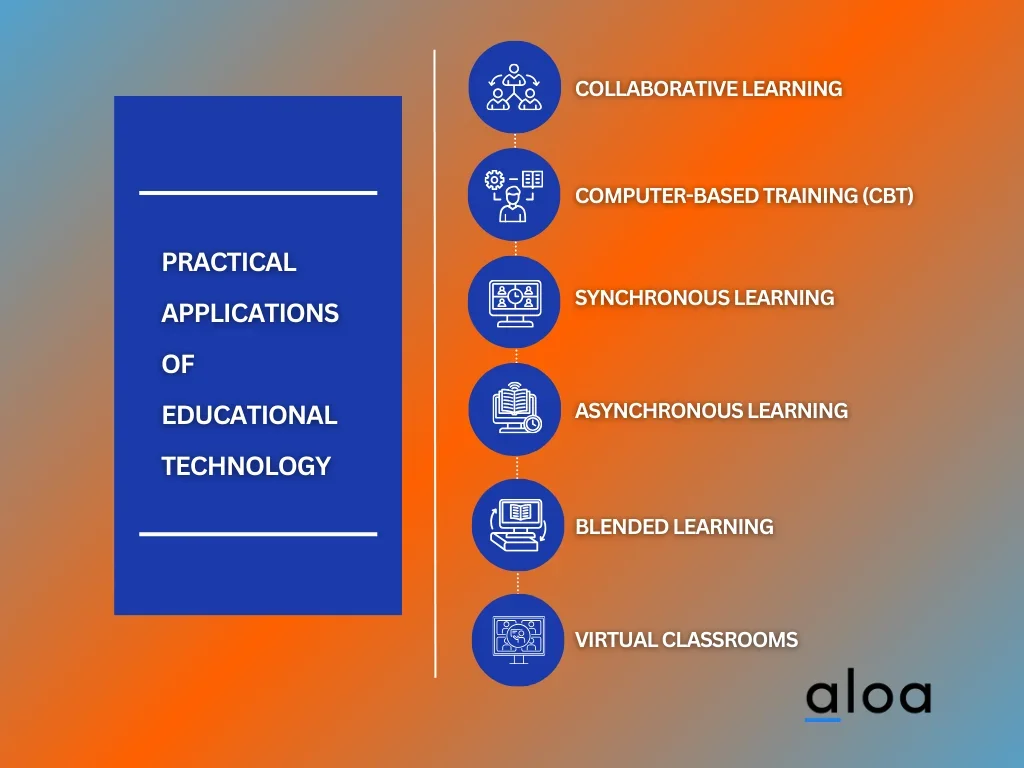
Collaborative Learning
Educational Technology promotes collaborative learning by enabling students and educators to connect and collaborate in virtual environments. Online discussion boards, video conferencing tools, and collaborative platforms facilitate group projects, discussions, and knowledge sharing, transcending geographical boundaries and fostering a sense of community among learners.
Computer-Based Training (CBT)
CBT leverages Educational Technology to deliver interactive and self-paced learning modules. It allows learners to acquire knowledge at their own pace, catering to diverse learning styles. Through simulations, quizzes, and multimedia content, CBT ensures engaging and compelling learning experiences.
Synchronous Learning
Synchronous learning occurs in real-time, facilitated by webinars and live video lectures streamed through a live transcoder and virtual classrooms. Educational technology allows students and instructors to interact and engage in discussions as if in a physical classroom, enhancing active participation and immediate feedback.
Asynchronous Learning
In contrast, asynchronous learning allows learners to access educational content conveniently. Video lectures, discussion boards, and course materials can be accessed anytime, accommodating various schedules and promoting self-directed learning.
Blended Learning
Blended learning combines traditional classroom instruction with online elements, offering a balanced approach to education. Educational technology is crucial in designing and managing blended learning environments and optimizing face-to-face and virtual interactions.
Virtual Classrooms
Virtual classrooms provide a dynamic and immersive learning experience. With interactive whiteboards, breakout rooms, and real-time assessments, Educational technology transforms traditional classrooms into engaging digital spaces, making education accessible to a broader audience.
Role of Software Development in Edtech
This relationship between Educational technology and software development has given rise to numerous innovative tools and platforms that revolutionize teaching and learning. Here, we list five crucial aspects of this relationship and delve into their significance:
Customized Learning Solutions
Software development is pivotal in creating tailored learning experiences. Through adaptive algorithms and data analytics, educational technology software can analyze individual students' progress and adapt content delivery accordingly. This personalized approach maximizes learning outcomes, ensuring students receive the suitable materials at the right pace.
Interactive Content
Educational Technology relies heavily on interactive content to engage students effectively. Software developers create interactive simulations, virtual labs, and gamified educational apps that make learning more enjoyable and immersive. Such interactive elements foster a more profound understanding and retention of knowledge.
Remote Learning
Educational Technology has accelerated the global shift towards remote and online learning. Software development enables the creation of robust online learning platforms, video conferencing tools, and collaboration apps that facilitate seamless remote education. This flexibility has become especially crucial during unforeseen events like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Data-Driven Insights
Edtech software collects vast amounts of data on student performance and engagement. Software developers create analytics tools that help educators make data-driven decisions. These insights enable teachers to identify struggling students early, assess the effectiveness of teaching methods, and refine curriculum design for improved learning outcomes.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Software development in Edtech has paved the way for more inclusive learning environments. Developers design software with accessibility features like screen readers, closed captioning, and speech recognition to accommodate diverse learning needs. This inclusivity ensures that education is accessible to all, regardless of disabilities or learning differences.
Key Takeaway
Staying updated with the latest technologies and methodologies is imperative in the software development industry. Edtech facilitates continuous learning and skill development among employees, helping them stay competitive and agile. It provides access to a wealth of online courses, tutorials, and certifications that can enhance the skill sets of software developers.
Moreover, educational technology aids in onboarding and training new hires, reducing the time and resources required. This, in turn, accelerates project timelines and boosts productivity.
To remain competitive and adaptable in the fast-paced world of software development, businesses and startups must prioritize integrating educational technology into their operations. Contact [email protected] to explore how Edtech can benefit your software development endeavors.

