You might have heard buzzwords like these from podcasts or tech news: "This AI platform leverages machine learning capabilities..." "They use ML-powered algorithms..."
But isn’t AI and ML the same thing? If you’ve ever asked that question, you’re not alone. Here's the frustrating reality: Many use these terms interchangeably. But when you can't distinguish between these technologies, you might choose the wrong solution for your problem.
At Aloa, we help businesses build custom AI and ML solutions that deliver measurable results. With 78% of organizations now using AI, understanding the difference between machine learning and artificial intelligence is now essential to staying competitive.
In this guide, we’ll explain the following:
- The definition of AI, ML, and deep learning
- How they relate to and differ from each other
- When to use each one
- Applications of AI and ML across various industries
Let’s dive in!
What is Artificial Intelligence?
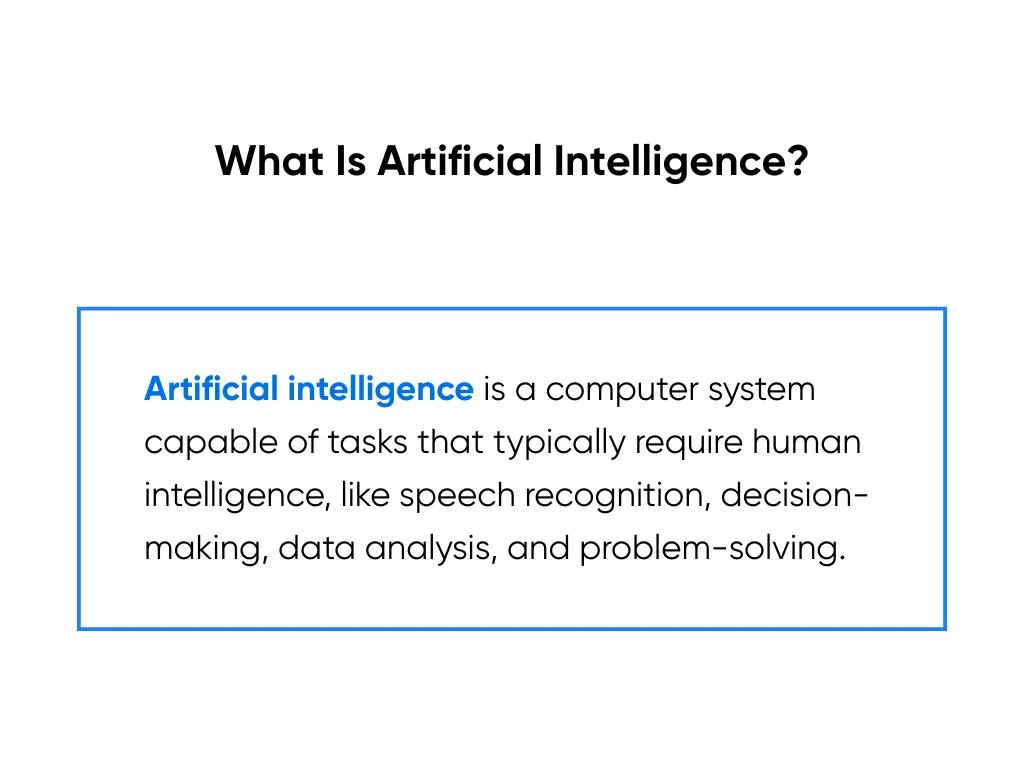
The first step to learning the difference between machine learning and artificial intelligence is establishing what AI is. Artificial intelligence refers to any computer system that can perform tasks traditionally requiring human intelligence, such as recognizing speech, making decisions, analyzing data, and solving problems.
Think of AI as a highly skilled assistant that never gets tired, can work 24/7, and can process vast amounts of information in seconds. It's like having a team of experts who can instantly review thousands of documents, spot patterns, and make recommendations
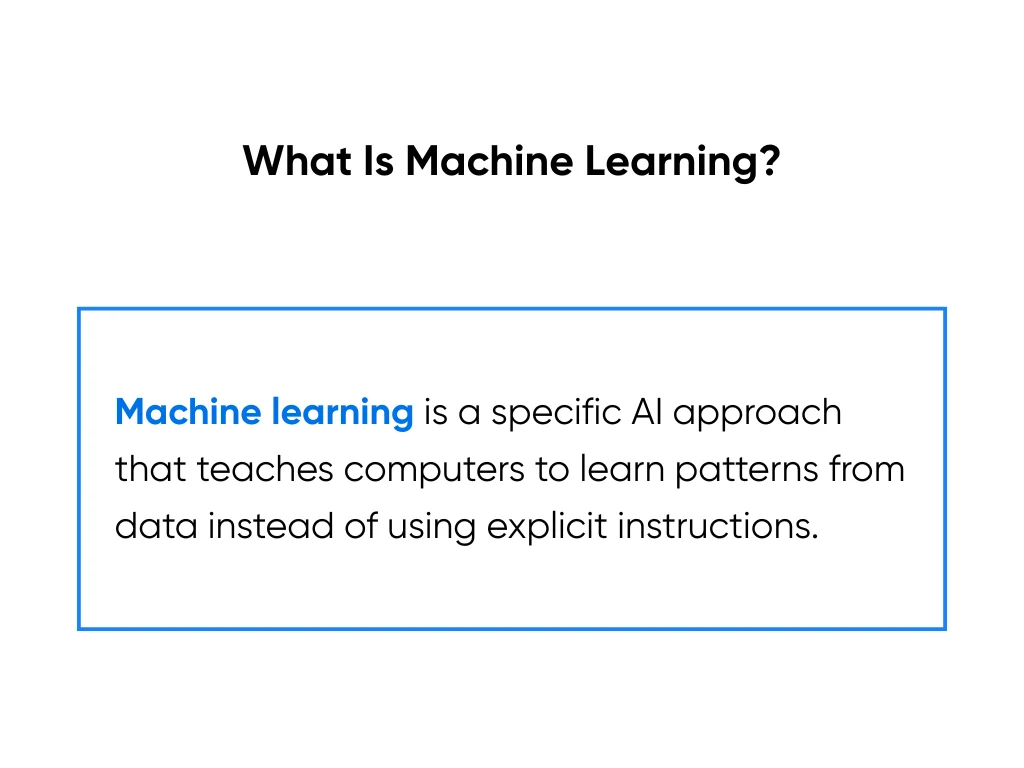
What Is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a specific AI approach that focuses on teaching computers to learn patterns from data rather than programming them with explicit instructions. Consider how you learned to recognize your friend's face: you didn't memorize a set of rules, but rather your brain automatically picked up on patterns after seeing them many times.
Traditional AI systems follow pre-written rules like a recipe, while machine learning systems develop their own understanding through experience. You can build AI systems using various methods that don't involve learning from data at all, but machine learning specifically requires training data and the ability to improve performance over time.
If you've ever seen ChatGPT reply with “Memory updated”, you've interacted with machine learning.
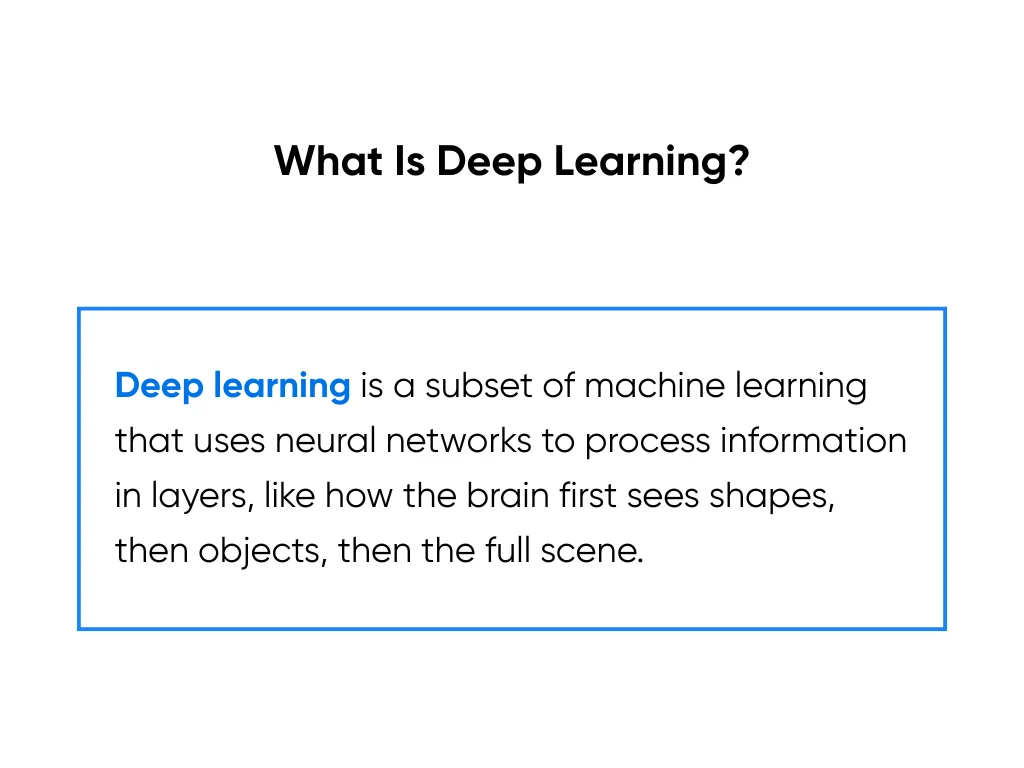
What Is Deep Learning?
Deep Learning is a specialized subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to process information in layers, similar to how the human brain works. This is similar to how your brain processes a complex image by first recognizing basic shapes, then combining them into objects, and finally understanding the entire scene.
While more resource-intensive than traditional machine learning, deep learning algorithms deliver breakthrough capabilities for specific complex tasks. For business applications, deep learning models excel at tasks like:
- Image recognition: Identifying products in photos for inventory management.
- Natural language processing: Understanding customer complaints and sentiment.
- Complex pattern recognition: Detecting sophisticated fraud patterns in financial transactions.
While more resource-intensive than traditional ML, deep learning algorithms deliver breakthrough capabilities in specific tasks and use cases.
The Difference Between Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: In-Depth
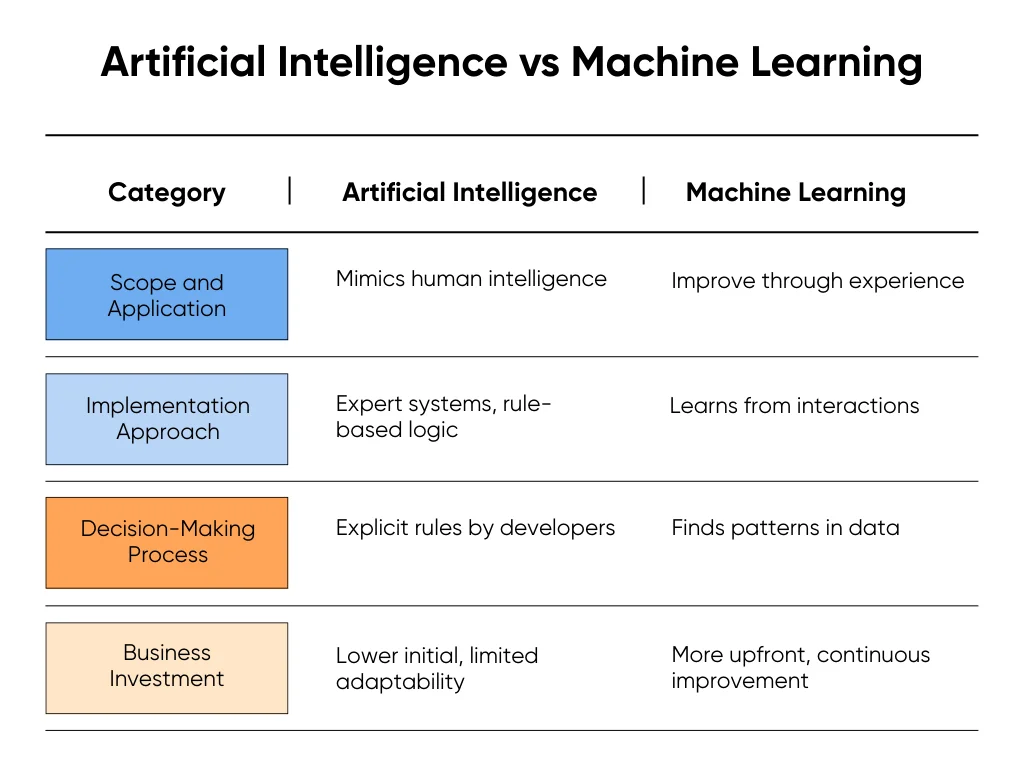
Understanding the difference between machine learning and artificial intelligence is crucial for making informed technology investments. TL;DR, AI is the umbrella term for any system exhibiting intelligent behavior. ML is a subset of AI that learns from training data to make predictions or decisions.
Scope and Application
Think of scope and application as the key difference between these two concepts. AI includes any technique that enables machines to mimic human intelligence. You can imagine AI as encompassing everything that makes a machine appear smart, regardless of how it achieves that intelligence.
ML specifically refers to systems that improve through experience, like how you get better at recognizing songs the more music you hear. For example, a chatbot that follows pre-programmed scripts is AI but not ML. A recommendation engine that learns from user behavior to suggest better products is both AI and ML.
Implementation Approach
AI can be implemented through various methods including expert systems, rule-based logic, and machine learning.
When you implement a basic customer service bot with scripted responses, you're using AI without ML. When that bot learns from customer interactions to provide better responses over time, you're incorporating ML.
Decision-Making Process
Traditional AI systems follow explicit rules programmed by developers. ML systems create their own rules by finding patterns in data.
This fundamental difference affects how each technology is deployed, maintained, and improved.
Rule-based AI requires manual updates when business rules change. ML systems adapt automatically as they receive new data.
Business Investment Considerations
AI implementations typically require lower initial investment for basic automation but offer limited adaptability.
ML requires more upfront investment in data preparation and model training but provides greater long-term value through continuous improvement.
According to industry data, companies see average implementation costs of $100,000-$500,000 for basic AI versus $200,000-$1 million for ML systems.
But how can a machine learn?
Like human learning, machine learning starts out with trial and error. Let's say developers are trying to teach a machine to draw a circle. The procedure will follow these basic steps:
- Machines don't start out knowing what circles are. They have to be given pointers in the form of examples to imitate or descriptions to go by.
- The developers give the program a basic algorithm to be able to make sense of examples and descriptions, and it attempts to draw a circle based on this information. If you've ever answered a Captcha, or those “are you a human?” security questions, you've helped give pointers to an ML program.
- The first attempts to draw a circle will be imperfect, but over time, they get better. The developers rate the program's performance based on how close it got to drawing a perfect circle.
- Since it remembers all of its previous attempts, it selects the ones that were rated the highest, and remembers what it did to achieve those results.
It's like training a new employee. You provide examples and feedback, and over time, they become better at their job.
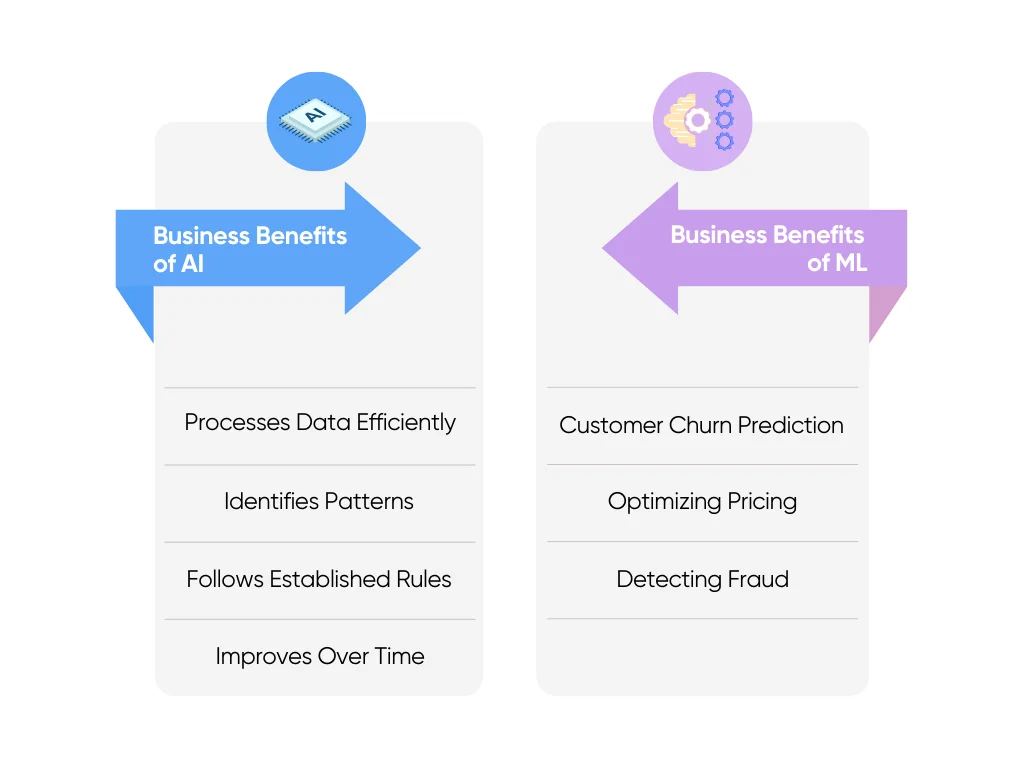
Business Benefits of AI vs. ML
So what does this all mean for your business? AI and ML each bring different advantages to the table. AI is great for automating processes and getting immediate results, while ML learns and gets smarter over time. The key is knowing which one fits your needs.
What AI Means for Businesses
We know that AI:
- Processes large amounts of data quickly and accurately
- Identifies patterns
- Makes decisions based on established rules
- Continuously improves performance over time
That sounds a lot like a top-performing robotic employee. Although it lacks the nuance, creativity, and ingenuity of humans, AI excels at efficiency. With AI, what traditionally took businesses weeks to analyze and act upon now happens in minutes through AI-powered automation and insights.
ML's Business Implications
The business value of ML lies in its ability to improve automatically. Being computer programs, ML systems can analyze millions of examples and learn patterns that humans might miss, becoming increasingly accurate at predictions and recommendations.
This is particularly powerful for complex tasks where the rules are difficult to define manually or where patterns change over time, such as:
- Customer churn prediction
- Optimizing pricing
- Detecting fraud
ML systems become more accurate as they process more data. This continuous improvement without constant reprogramming makes ML ideal for dynamic business environments where conditions and patterns evolve.
How to Decide: Choosing AI, ML, or Both
Selecting between AI and ML—or implementing both—requires careful evaluation of your business needs, resources, and objectives.
Microsoft's AI Decision Framework suggests starting with your specific use case: individual productivity enhancement benefits from AI assistants, while predictive analytics requires ML capabilities.
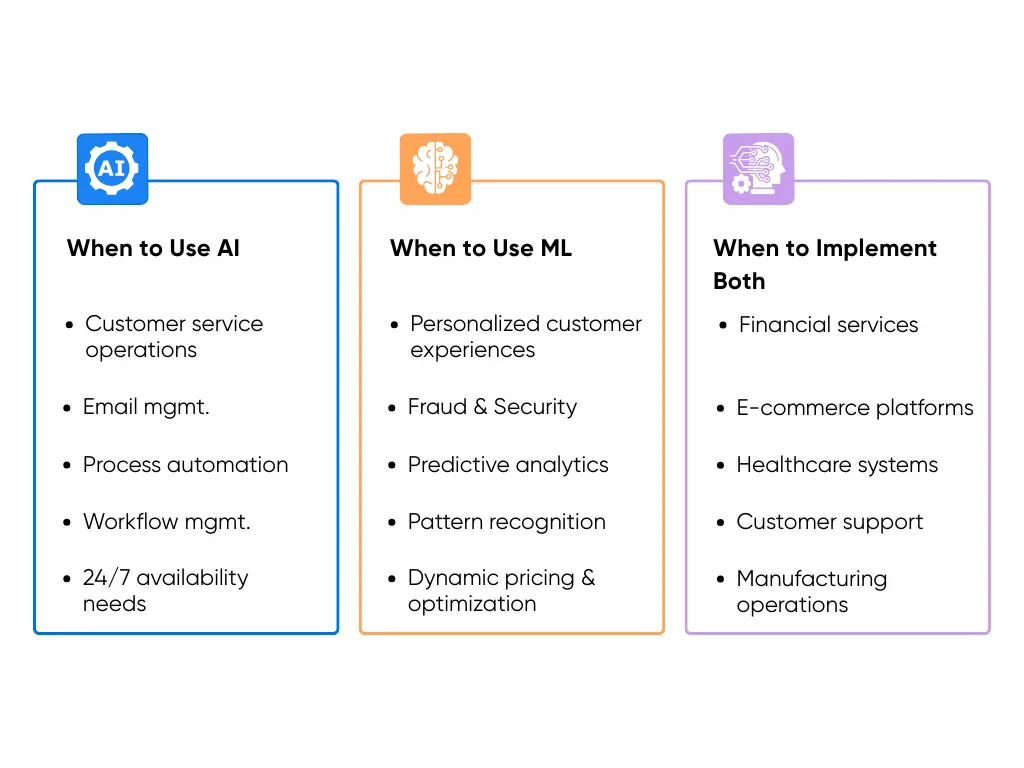
When to Use Artificial Intelligence
AI incorporates a mix of various technologies, which can include ML. Think of it as the Swiss Army knife to ML's screwdriver. It's best implemented in situations where you need various systems working in concert.
Implement AI when you need to automate routine, rule-based tasks with clear logic:
- Customer service operations: Deploy chatbots for FAQs, automated ticket routing, and standard support workflows that follow predictable patterns
- Email management: Automate responses to common inquiries, sort incoming messages by priority, and trigger follow-up sequences based on customer actions
- Process automation: Streamline invoice processing, appointment scheduling, data entry, and document routing between departments
- Workflow management: Coordinate multi-step business processes, send automatic notifications, and ensure tasks move through approval chains
- 24/7 availability needs: Provide consistent service outside business hours through automated systems that handle routine requests and escalate complex issues
If your processes are well-defined with clear decision trees and your business requires consistent, round-the-clock availability, traditional AI provides immediate value and measurable efficiency gains.
When to Use Machine Learning
Machine learning is fairly self-explanatory if you think of it like business software that learns with you. Use it when you need to predict future outcomes, personalize experiences at scale, or detect complex patterns in dynamic environments where rules are difficult to define or constantly changing.
Deploy ML when you need systems that continuously learn and adapt:
- Personalized customer experiences: Create dynamic product recommendations, customized content feeds, and tailored marketing campaigns that improve based on individual user behavior (like Spotify's Radio feature)
- Fraud detection and security: Identify suspicious transaction patterns, detect unusual account activity, and flag potential security threats by learning from historical data and emerging attack methods
- Predictive analytics: Forecast consumer demand, predict equipment maintenance needs, estimate customer lifetime value, and anticipate market trends using historical patterns
- Pattern recognition: Analyze complex datasets to discover hidden insights, identify market opportunities, and detect anomalies that traditional rule-based systems would miss
- Dynamic pricing and optimization: Adjust pricing strategies in real-time, optimize inventory levels, and fine-tune operations based on constantly changing market conditions
ML excels in scenarios where you need an intelligent assistant that constantly monitors everything, builds knowledge over time, and adapts to new information without requiring manual rule updates.
When to Implement Both
Many successful implementations combine AI and ML to leverage the strengths of both approaches. Start with AI for immediate automation benefits, then layer ML capabilities for continuous improvement and intelligent adaptation.
Deploy both AI and ML when you need comprehensive intelligent systems:
- Financial services: Use AI for automated transaction processing and rule-based compliance checks, while ML analyzes spending patterns for fraud detection and credit risk assessment (Mastercard achieved 20% improvement in fraud detection using this hybrid approach)
- E-commerce platforms: Implement AI for automated inventory management and order processing, combined with ML for personalized product recommendations and dynamic pricing optimization
- Healthcare systems: Apply AI for standardized patient intake and appointment scheduling, while ML analyzes medical records for diagnostic support and treatment outcome predictions
- Customer support: Deploy AI chatbots for routine inquiries and ticket routing, enhanced by ML that learns from interaction patterns to improve response quality and predict escalation needs
- Manufacturing operations: Use AI for automated quality control and production line management, supplemented by ML for predictive maintenance and supply chain optimization
This hybrid approach allows organizations to capture immediate efficiency gains from AI automation while building long-term competitive advantages through ML's adaptive learning capabilities.
Resource and Timeline Considerations
- AI implementations typically deploy in 2-4 months with faster ROI (6-12 months).
- ML projects require 4-8 months for initial deployment with ROI in 12-18 months but offer exponential long-term value.
Consider your timeline urgency, available data quality, technical team capabilities, and budget constraints when deciding.
Industry-Specific Examples of AI and ML Implementation
Finance: From fraud detection to customer insights
The finance sector leads in AI and ML adoption, with implementations delivering billions in value. For example:
- The U.S. Treasury Department: Prevented or recovered $4 billion in FY2024 using ML algorithms for fraud detection, up from $652.7 million the previous year. Their AI analyzes 1.4 billion payments annually at massive scale.
- JPMorgan Chase: Achieved a 95% reduction in false positives for anti-money laundering and a 50% overall reduction in false positive alerts. Their ML system analyzes transaction patterns and user behavior in real-time across millions of transactions.
- Mastercard: Scans 1 trillion data points to achieve up to 300% improvement in fraud detection. Their system identifies compromised cards before fraudulent use with double the previous detection rate.
Healthcare: Improving patient care and operational efficiency
Healthcare organizations use AI and ML to address physician burnout while improving patient care.
- AdventHealth: Implemented Nuance DAX Copilot across nearly 2,000 physicians, with 86% reporting reduced burnout and 80% noting improved patient experience. This AI automatically documents patient encounters using ambient voice technology.
- St. Luke's Health System: Generated $13,049 in additional revenue per clinician annually with Ambience Healthcare's AI platform. Their implementation reduced documentation time by 39% and decreased time to chart closure by 41%.
- Northwestern Medicine: Physicians saw 11.3 additional patients monthly while spending 24% less time on notes thanks to Microsoft's DAX Copilot from Nuance Communications.
These healthcare implementations exemplify how effective Aloa's approach to AI implementation is. Focusing on measurable business outcomes rather than technology for its own sake is what truly allows AI to reach its full potential.
Retail: Personalizing customer experiences at scale
Retail giants leverage AI and ML to transform customer experiences and operations.
- Amazon's Rufus AI: Amazon's AI shopping assistant, available to all U.S. customers, processes 3 million tokens per minute during peak events like Prime Day.
- Walmart: Their ML-driven personalization and generative AI search capabilities serve 255 million weekly customers, while AI-powered associate tools reduced shift planning time from 90 to 30 minutes. Their multi-touchpoint AI strategy achieved a 38% increase in customer satisfaction scores.
- Tesco's Clubcard AI: Powered by EagleAI, this personalized loyalty program issues 289 million personalized coupons each year to 23 million members. The platform makes 190+ intelligent decisions per customer, contributing to 10% profit growth.
Common Misconceptions About AI vs. ML
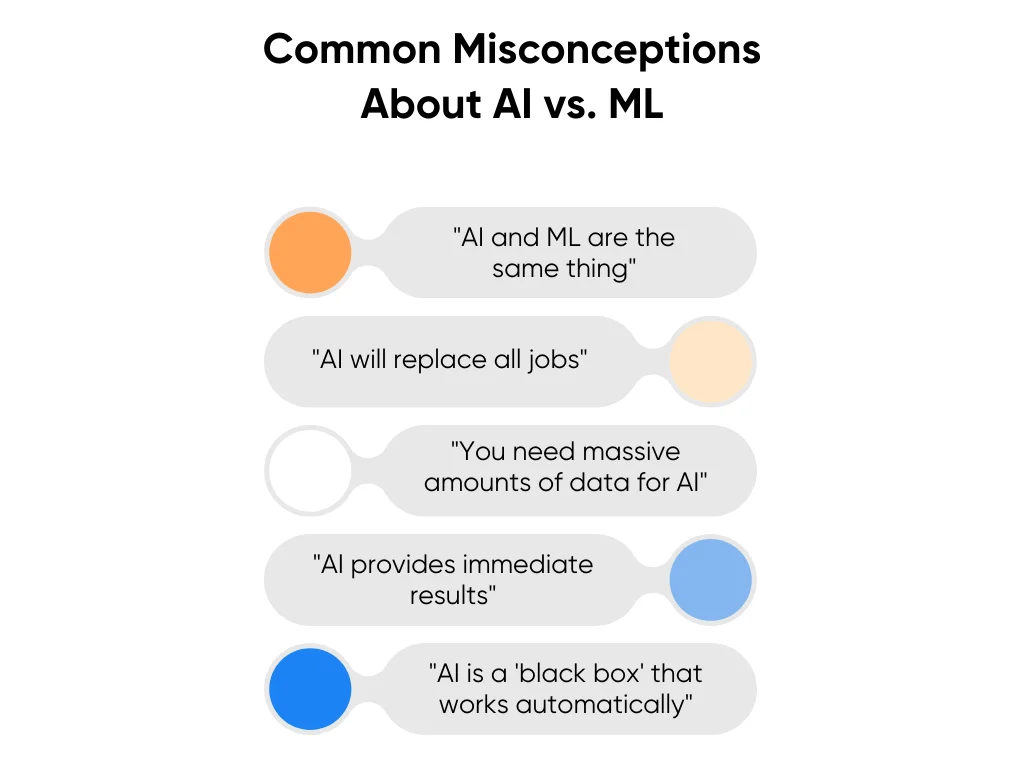
"AI and ML are the same thing"
Remember, AI is the broad concept of machines exhibiting intelligent behavior, while ML is a specific technique within AI where systems learn from data.
AI is artificial or machine intelligence, and machine learning is one way to achieve that intelligence.
A rule-based chatbot is AI but not ML, because it just reads off a set of rules to know what reply to give. It doesn't “learn” anything new.
Whereas a fraud detection system that improves its accuracy over time uses both AI and ML.
"AI will replace all jobs"
Research consistently shows AI augments rather than replaces human workers. PwC's 2025 Global AI Jobs Barometer found that job availability grew 38% in roles more exposed to AI, with workers seeing a 56% wage premium for AI skills.
Additionally, a recent MIT Sloan study reveals AI is more likely to complement human labor, not substitute it, with newly added tasks requiring stronger human capabilities.
Successful healthcare implementations like AdventHealth's AI tools are perhaps the best examples. AI can't replace doctors, but by automatically handling charting and other busywork, they can make doctors much more effective.
"You need massive amounts of data for AI"
While some ML applications benefit from large datasets, many practical business applications work effectively with focused, high-quality data. German research institute Fraunhofer IPK demonstrates how businesses can start with smaller datasets and scale gradually. Quality matters more than quantity.
"AI provides immediate results"
Effective AI implementation requires careful planning and realistic timelines. Industry data shows proof of concepts typically require 4-6 weeks, with full implementation taking several months.
The U.S. Treasury's fraud detection system didn't achieve $4 billion in recoveries overnight. To reach current performance levels, it implemented systematic development, testing, and refinement.
"AI is a 'black box' that works automatically"
Effective AI systems require continuous human oversight, monitoring, and improvement.
Stanford's AI Index Report emphasizes that successful AI implementations involve data scientists framing problems, preparing data, removing bias, and interpreting results.
AI enhances human decision-making rather than replacing it entirely.
Aloa's Approach: From Concept to Deployment
At Aloa, we've seen businesses struggle with the same AI implementation challenges: choosing the right technology, managing data quality, and ensuring practical results. Our approach addresses these pain points head-on with strategic, measurable solutions.
Choosing the Right Technology
Many businesses struggle with whether to implement AI, ML, or both. We specialize in developing agentic AI solutions that enhance business efficiency, optimize workflows, and improve customer interactions. We help determine whether you need traditional AI for immediate automation or ML systems that adapt over time.
Ensuring Quality Data and Realistic Timelines
The biggest misconception is that AI provides instant results or requires massive datasets. We build custom AI solutions that drive real business outcomes, delivering measurable value and competitive advantage. We focus on high-quality data and realistic implementation timelines, helping businesses scale gradually.
Delivering Practical Solutions That Work
We transform business operations with custom AI solutions, building intelligent internal tools and applications that streamline workflows, enhance decision-making, and drive efficiency. From computer vision to generative AI, we build tools that deliver measurable results while complementing existing operations.
FAQs About the Difference Between Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
How much data do I need to start an ML project?
Quality is better than quantity in ML implementations. Successful business projects often start with thousands of high-quality, relevant records rather than millions. Focus on clean, labeled data representing your specific use case. Many successful ML projects in finance and healthcare started with 10,000-50,000 focused records.

How do machine learning models learn from examples?
ML models look at patterns: trends, correlations, and anomalies. Image recognition is essentially recognizing patterns in pixel arrangements. Once an ML system learns basic patterns, it applies that understanding to new challenges faster. Each capability builds on previous learning, making your investment more valuable over time.
What's the typical ROI timeline for AI vs ML investments?
AI shows ROI within 6-12 months through immediate efficiency gains. ML requires 12-18 months but offers exponential long-term value. St. Luke's recovered their ML investment in 5 months, while Northwestern Medicine achieved 112% ROI within the first year.
Can I use AI without ML, or do they always go together?
You can absolutely use AI without ML. Many successful implementations use rule-based AI for automation and customer service. However, combining both often delivers the best results—AI for immediate automation, ML for continuous improvement.
How do I know if my problem needs AI or ML specifically?
If your problem has clear rules, use traditional AI. If it involves predictions, patterns, or personalization, you need ML. Use AI for "respond with store hours," ML for "predict customer churn."
What are the main technical requirements for ML implementation?
ML requires quality data, computational resources, and skilled personnel. Cloud platforms like AWS often provide sufficient resources without massive infrastructure investment. Many organizations partner with specialized firms to access these capabilities.
How does deep learning differ from regular ML?
Deep learning uses neural networks with multiple layers for complex pattern recognition. Regular ML works well for structured data, deep learning excels with unstructured data like images or text. Use regular ML for predictive analytics, deep learning for specialized tasks.
What industries benefit most from AI and ML?
Finance, healthcare, and retail show the highest ROI. Finance leads with fraud detection, healthcare transforms through clinical documentation, retail excels in personalization. Manufacturing, logistics, and professional services also show strong adoption rates.
Key Takeaways
Knowing the difference between machine learning and artificial intelligence, and when to use each, directly impacts your strategy and ROI. AI provides immediate automation benefits, while ML delivers adaptive learning that creates long-term competitive advantage. The best approach often combines both technologies.
Successful implementations follow clear patterns:
- Start with defined problems.
- Focus on augmenting human capabilities.
- Measure tangible business outcomes.
Companies like JPMorgan and St. Luke's achieved measurable results by aligning technology choice with specific business objectives.
Ready to transform your business with AI and ML? Learn more about Aloa's AI and machine learning development services and discover how we can help you build solutions that actually work.

![Difference Between Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence [Essential Guide]](https://images.aloa.co/posts/differences-between-machine-learning-artificial-intelligence-and-deep-learning/%20Understanding%20the%20Difference%20Between%20Machine%20Learning%20and%20Artificial%20Intelligence%20A%20Business%20Leader_s%20Guide.webp)